美洲蛇鹈
| 美洲蛇鹈 化石时期:
| |
|---|---|

| |
| 雄鸟 | |
| 科学分类 | |
| 界: | 动物界 Animalia |
| 门: | 脊索动物门 Chordata |
| 纲: | 鸟纲 Aves |
| 目: | 鰹鳥目 Suliformes |
| 科: | 蛇鹈科 Anhingidae |
| 属: | 蛇鹈属 Anhinga |
| 种: | 美洲蛇鹈 A. anhinga
|
| 二名法 | |
| Anhinga anhinga (Linnaeus, 1766)
| |
| 亚种 | |
|
A. a. anhinga | |
| |
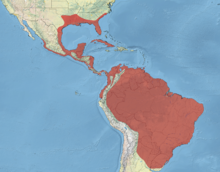
| 分布图: 繁殖区 留鸟
| |
| 異名 | |
|
Plotus anhinga Linnaeus, 1766 | |
美洲蛇鹈(学名:Anhinga anhinga;英语:anhinga、snakebird、darter、American darter、water turkey)是蛇鹈属的一种鸟类,分布于美洲温暖地区。“anhinga”这个词来自巴西图皮语,意思是“恶魔鸟”或“蛇鸟”。
分布
[编辑]它分为两个亚种A. a. anhinga、A.a. leucogaster。前者主要分布在南美洲的安第斯山脉以东和特立尼达和多巴哥群岛。后者发现于美国南部、墨西哥、古巴和格林纳达[2]。
特征
[编辑]
美洲蛇鹈是一种大型鸟类,体长约89 cm(35英寸),翼展1.14米(3.7英尺)[3][4]。A. a. anhinga比A. a. leucogaster略大。体重约为1.22公斤(2.7磅)[4][5][6]。喙的长度是头部的两倍,和脚蹼一样呈黄色[7][8][3][5]。除了头部、颈部和上胸部颜色较浅之外,雌性美洲蛇鸟与雄性没有什么区别[9][10]。由于长相相似,它常与角鸕鶿混淆。美洲蛇鹈尾羽更宽更长,且喙尖锐,不像角鸬鹚一样有勾[11]。
习性
[编辑]其羽毛不防水,因此不能长时间漂浮在水面上,但有利于下潜捕食[12]。羽毛湿掉的美洲蛇鹈不能远距离飞行,但可以短暂低飞一段时间。它们会张开翅膀站立,以晒干羽毛并恢复体温[13]。
食物
[编辑]它以中等大小的湿地鱼类、 两栖动物、水生无脊椎动物和昆虫为食[14][4]。它们会在在水下追踪猎物,用喙将其穿刺,再带出水面,然后吞食。[15]
保护状况
[编辑]它们在美国受《候鸟条约法》(Migratory Bird Treaty Act of 1918)保护[16],但其数量并不堪忧。[1]
参考文献
[编辑]- ^ 1.0 1.1 BirdLife International. Anhinga anhinga. The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016, 2016: e.T22696702A93581588 [13 November 2021]. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22696702A93581588.en
 .
.
- ^ Blake, Emmet Reid. Birds of Mexico: a guide for field identification
 . University of Chicago Press. 1953: 151–152. ISBN 0-226-05641-4.
. University of Chicago Press. 1953: 151–152. ISBN 0-226-05641-4.
- ^ 3.0 3.1 Sibley, David Allen. The Sibley Field Guide to Birds of Eastern North America. New York: Alfred A. Knopf. 2003: 45. ISBN 0-679-45120-X.
- ^ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Template:Cite AllAboutBirds
- ^ 5.0 5.1 Maehr, David S.; Kale, H.W.; Kale, II, Herbert W. Florida's Birds: A Field Guide and Reference. Pineapple Press Inc. 2005: 33, 38. ISBN 1-56164-335-1.
- ^ Hennemann, III, Willard W. Energetics, Behavior and the Zoogeography of Anhingas and Double-Crested Cormorants. Ornis Scandinavica (Wiley). December 1985, 16 (4): 319–323. JSTOR 3676697. doi:10.2307/3676697.
- ^ Robbins, Samuel D. Wisconsin Birdlife: Population and Distribution Past and Present. University of Wisconsin Press. 1991: 127–128. ISBN 978-0-299-10260-9.
- ^ Audubon, John James. The Birds of America. J.B. Chevalier. 1843: 443–457.
- ^ Burton, Maurice; Burton, Robert. International Wildlife Encyclopedia
 . Marshall Cavendish. 2002: 646. ISBN 0-7614-7271-1.
. Marshall Cavendish. 2002: 646. ISBN 0-7614-7271-1.
- ^ Gregware, Bill; Gregware, Carol. Guide to the Lake Okeechobee Area. Pineapple Press Inc. 1997: 54. ISBN 1-56164-129-4.
- ^ Peterson, Roger Tory. A Field Guide to the Birds of Texas. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. 1998: 130. ISBN 0-395-92138-4.
- ^ Anhinga - Introduction. Birds of North America Online. [2018-12-08]. (原始内容存档于2018-06-05) –通过website: birdsna.org (英语).
- ^ Hennemann, Willard W. "Energetics and Spread-Winged Behavior of Anhingas in Florida (页面存档备份,存于互联网档案馆)" The Condor84, no. 1 (1982): 91-96.
- ^ Kearns, Laura. ADW: Anhinga anhinga: INFORMATION. Animaldiversity.org. [2022-08-08]. (原始内容存档于2022-08-05).
- ^ Owre, Oscar, T. Adaptations for locomotion and feeding in the Anhinga and the Double-crested cormorant (PDF). Ornithological Monographs (American Ornithologists Union). 1967: 126–127 [2022-09-11]. ISBN 978-0-9436-1006-1. JSTOR 40166666. doi:10.2307/40166666. (原始内容存档 (PDF)于2022-05-17).
- ^ U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. Birds Protected by the Migratory Bird Treaty Act. 1995 [15 September 2008]. (原始内容存档于8 May 2008).