异香草醛
外观
| 异香草醛 | |
|---|---|
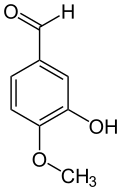
| |
| IUPAC名 3-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde[1] | |
| 别名 | 5-Formylguaiacol 3-Hydroxy-p-anisaldehyde |
| 识别 | |
| CAS号 | 621-59-0 |
| PubChem | 12127 |
| ChemSpider | 11629 |
| SMILES |
|
| Beilstein | 1073021 |
| EINECS | 210-694-9 |
| RTECS | CU6540000 |
| MeSH | Isovanillin |
| 性质 | |
| 化学式 | C8H8O3 |
| 摩尔质量 | 152.15 g·mol−1 |
| 外观 | 半透明晶体 |
| 熔点 | 115 °C(388 K)[2] |
| 沸点 | 179 °C(452 K)(15 mmHg) 135—145 °C(408—418 K)(0.02 Torr)[3] |
| log P | 1.25 |
| pKa | 9.248 |
| 危险性 | |
| 警示术语 | R:R36/37/38 |
| 安全术语 | S:S26, S36/37 |
| 欧盟分类 | |
| 相关物质 | |
| 相关化学品 | 茴香醛 |
| 若非注明,所有数据均出自标准状态(25 ℃,100 kPa)下。 | |
异香草醛(英语:Isovanillin;又称异香兰素)是一种酚醛,香草醛的同分异构体之一[4]。它是醛氧化酶的一种选择性抑制剂,能被醛脱氢酶代谢成异香草酸,这种特性使得异香草醛能够用于酒精厌恶疗法[5]。异香草醛可以作为吗啡全合成的前体[6][7]。文献中已有描述其(和香草醛)在大鼠体内可能的代谢过程[8][9]。
参见
[编辑]参考资料
[编辑]- ^ Isovanillin. The PubChem Project. National Center for Biotechnology Information. [2021-04-20]. (原始内容存档于2012-11-03).
- ^ Angela M. Bernard, M. Rossella Ghiani, Pier Paolo Piras, Antonio Rivoldini. Dealkylation of Activated Alkyl Aryl Ethers Using Lithium Chloride in Dimethylformamide. Synthesis. 1989, 1989 (04): 287–289 [2021-04-21]. ISSN 0039-7881. doi:10.1055/s-1989-27225. (原始内容存档于2018-06-03) (英语).
- ^ Schwarz, R.; Capek, K. A new synthesis of homoisovanillic acid and of isovanillin. Monatshefte fuer Chemie, 1952. 83: 883-893. ISSN: 0026-9247.
- ^ isovanillin - Compound Summary (CID 12127). [2021-04-20]. (原始内容存档于2013-12-27).
- ^ Georgios Panoutsopoulos; Christine Beedham. Enzymatic Oxidation of Vanillin, Isovanillin and Protocatechuic Aldehyde with Freshly Prepared Guinea Pig Liver Slices. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2005, 15 (1–4): 89–98 [2021-04-20]. PMID 15665519. S2CID 17057295. arXiv:quant-ph/0403227
 . doi:10.1159/000083641. (原始内容存档于2011-06-15).
. doi:10.1159/000083641. (原始内容存档于2011-06-15).
- ^ Uchida, Kenji; Yokoshima, Satoshi; Kan, Toshiyuki; Fukuyama, Tohru. Total Synthesis of (±)-Morphine. Organic Letters. 2006, 8 (23): 5311–5313. PMID 17078705. doi:10.1021/ol062112m.
- ^ Uchida, Kenji; Yokoshima, Satoshi; Kan, Toshiyuki; Fukuyama, Tohru. Total Synthesis of (±)-Morphine. Heterocycles. 2009, 77 (2): 1219–1234 [27 December 2013]. PMID 17078705. doi:10.3987/COM-08-S(F)103.
- ^ Strand, L. P.; Scheline, R. R. The metabolism of vanillin and isovanillin in the rat. Xenobiotica; the Fate of Foreign Compounds in Biological Systems. January 1975, 5 (1): 49–63. ISSN 0049-8254. PMID 1154798. doi:10.3109/00498257509056093.
- ^ Vanillin and isovanillin metabolism. WikiPathways. 2019-10-31. (原始内容存档于2021-04-20).
