氨三乙腈
| 氨三乙腈 | |
|---|---|

| |
| IUPAC名 2,2′,2′′-Nitrilotriacetonitrile | |
| 别名 | 三(氰甲基)胺 2,2',2''-氮川三乙腈 |
| 识别 | |
| CAS号 | 7327-60-8 |
| PubChem | 81762 |
| ChemSpider | 73778 |
| SMILES |
|
| InChI |
|
| InChIKey | LJAIDEYQVIJERM-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| 性质 | |
| 化学式 | C6H6N4 |
| 摩尔质量 | 134.14 g·mol−1 |
| 熔点 | 125 °C(398 K)[1] |
| 结构 | |
| 空间群 | Pnma |
| 晶格常数 | a = 7.1085, b = 9.9320, c = 9.3869 |
| 危险性 | |
GHS危险性符号  
| |
| GHS提示词 | 危险 |
| H-术语 | H301, H302, H312, H315, H319, H335, H373 |
| P-术语 | P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+310, P301+312, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P314, P321 |
| 若非注明,所有数据均出自标准状态(25 ℃,100 kPa)下。 | |
氨三乙腈(NTAN)是一种有机化合物,化学式为C6H6N4,它是氨三乙酸、三(氨乙基)胺和氨乙基哌嗪的前驱体。
合成
[编辑]氨三乙腈可由甲醛、氨和氰化氢在酸性水溶液中通过氨的氰甲基化反应得到。[2][3]
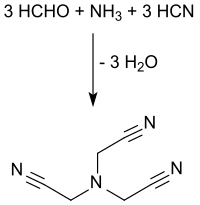
氨气进入反应体系,以六亚甲基四胺[4]或硫酸铵的形式和甲醛水溶液(通常为37wt%)在pH<2的调节下与氰化氢在100 °C反应得到。[5]在生产过程中,尤其是连续反应的情况下,低于90 °C时,氨三乙腈会沉淀出来,堵塞反应器管路,导致热失控。 [6]
应用
[编辑]在碱性催化剂(如甲醇钠)存在下,氨三乙腈可与亚氨基二乙腈在熔体中均聚或共聚,形成深色的固体聚合物,它在1000°C以上可碳化形成含氮导电聚合物。[7]
氨三乙腈在氢化时,其中一个氰基会转化为亚氨基,相比于亚氨基的进一步氢化,它倾向于进攻另一个相邻的氰基以形成稳定的六元环。催化氢化的最终产物是氨乙基哌嗪。

在雷尼镍等催化剂存在下、氨过量时进行氢化,氨三乙腈会转化为三(氨乙基)胺[8]。

得到的这种化合物(简写tren)可用作四齿配体和过渡金属离子形成稳定的螯合物。[9]
氨三乙腈和甲醛在pH 9.5下反应,得到2,2-二羟甲基氨三乙腈,它在氢氧化钠溶液中于100 °C水解,得到2,2-二羟甲基氨三乙酸三钠,酸化后得到2,2-二羟甲基氨三乙酸。[10]

该化合物可作为重金属离子或碱土金属离子的络合剂,如作为漂白剂(过硼酸钠等)的稳定剂和作为洗涤助洗剂,用于抑制纺织品在洗涤过程中产生水垢。
氨三乙腈在硫酸中水解,可以定量产生氨三乙酰胺,它可用作金属配位的中性四齿配体。[11]升高温度,通过闭环反应可以得到3,5-二氧代哌嗪-1-乙酰胺,中和后在过量氨水中加热,也可以定量转化为氨三乙酰胺。[12][13]
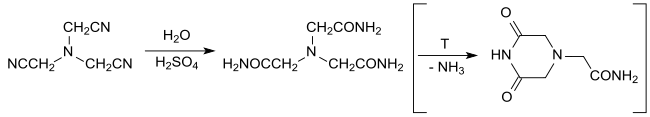
氨三乙腈在酸性或碱性条件下水解,可以得到氨三乙酸及其钠盐。[14][2]反应中可能产生的CN−可以通过氧化后处理(如在pH 8下使用次氯酸钠氧化)去除。[15]

它和盐酸羟胺、氢氧化钠在乙醇水溶液中反应,可以得到四齿配体氮三乙酰胺肟,它可以螯合Cu2+。[16]
参考文献
[编辑]- ^ Dubsky, J. V.; Wensink, W. D. Direct nitration of aliphatic imino compounds. II. Action of absolute nitric acid on 3,5-diketo-1-acetamidohexahydro-1,4-diazine. Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 1916, 49: 1041–1044. ISSN 0365-9496.CODEN BDCGAS
- ^ 2.0 2.1 US 3337607,J.C. Wollensak,“Process for preparation of an amine nitrile”,发表于1967-08-22
- ^ US 3840581,H. Neumaier, W. Vogt, K. Sennewald, R. Schuller, G. Lenz,“Process for the manufacture of nitrilotriacetonitrile”,发表于1974-10-08
- ^ US 3061628,J.J. Singer Jr., M. Weisberg,“Process and preparation of amino nitriles and acetic acids”,发表于1962-10-30
- ^ EP 0102343,C.Y. Shen,“Process for producing nitrilotriacetonitrile”,发表于1986-02-26
- ^ E. Fiedler, Emergency Runaway Reaction – What Precedes? What Follows?, Chem. Engineer. Transactions (CET) 48, 2016, 48: 361–366, ISBN 978-88-95608-39-6, doi:10.3303/CET1648061
- ^ US 3578643,L.L. Wood, R.A. Hamilton,“New polymers from nitrilotriacetonitrile and iminodiacetonitrile”,发表于1971-05-11
- ^ US 3565957,S.B. Mirviss, D.J. Martin, E.D. Weil,“Hydrogenation of nitrilotriacetonitrile”,发表于1971-02-23
- ^ G. Anderegg; V. Gramlich, 1:1 Metal Complexes of Bivalent Cobalt, Nickel, Copper, Zink, and Cadmium with the Tripodal Ligand tris[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]amine: Their stabilities and the X-ray crystal structure of its copper(II) complex sulfate, Helv. Chim. Acta 77 (3), 1994, 77 (3): 685–690, doi:10.1002/hlca.19940770312
- ^ EP 0396999,A. Oftring, S. Birnbach, R. Bauer, C. Gousetis, W. Trieselt,“2-Methyl- und 2-Hydroxymethyl-serin-N,N-diessigsäure und ihre Derivate”,发表于1990-11-14
- ^ D.A. Smith; S. Sucheck; S. Cramer; D. Baker, Nitrilotriacetamide: Synthesis in concentrated sulfuric acid and stability in water, Synth. Commun. 25 (24), 1995, 25 (24): 4123–4132, doi:10.1080/00397919508011491
- ^ GB 1170399,“A process for preparing 3,5-dioxo-1-piperazineacetamide and nitrilotriacetic acid triamide”,发表于1969-11-12
- ^ D.A. Smith; S. Cramer; S. Sucheck; E. Skrzypzak-Jankun, Facile synthesis of substituted nitrilotriacetamides, Tetrahedron Lett. 33 (50), 1992, 33 (50): 7765–7768, doi:10.1016/0040-4039(93)88040-P
- ^ US 4547589,C.Y. Shen,“Hydrolysis of nitrilotriacetonitrile”,发表于1985-10-15
- ^ US 8362298,O.M. Falana, A. Hikem, S.R. Kakadjian, F. Zamora,“Hydrolyzed nitrilotriacetonitrile compositions, nitrilotriacetonitrile hydrolysis formulations and methods for making and using same”,发表于2013-01-29
- ^ Pearse, George A.; Raithby, Paul R.; Maughan, Maria M.J. Synthesis and x-ray crystal structure of 2,2′,2″-iminotris(acetamidoxime) copper(II) sulphate monohydrate, [CuN(CH2CNH2:NOH)3(SO4)]·H2O. Polyhedron. 1994-01, 13 (4): 553–558 [2022-08-02]. ISSN 0277-5387. doi:10.1016/S0277-5387(00)84731-2. (原始内容存档于2018-06-26).
